How to Expand Your Ecommerce Business into a New Country
Many U.S. ecommerce businesses have considered selling across borders at some point. At the same time, many consumers have looked at products abroad that they wish they could purchase at home. It might surprise you to learn that more than half (57%) of global online shoppers already make purchases from overseas retailers, according to Nielsen.
The opportunity brings along many challenges for ecommerce retailers. What countries should you target? How do you market to non-local buyers? How do you handle translation, currencies, payment options, fulfillment and other technical and logistical issues? These questions are enough to keep most businesses on the sidelines — missing out on huge opportunities.
Let's take a look at practical ways to expand your ecommerce business into a new country.
Getting Started
The best way to determine potential expansion opportunities is to look at your existing customer base. If you're already shipping to some countries, you may want to consider targeting them with local payment methods, better shipping methods, and/or marketing campaigns. If you receive a lot of foreign visitors, those countries may be a good first step.
The next step is researching these markets to see what would be involved in selling to them using tools like Export.gov, the Small Business Administration (SBA), and other resources. In particular, you should look for information on tariffs, taxes, import restrictions, local preferences and other factors that could influence product demand or delivery logistics.
Some important questions to ask include:
- What types of products do local customers buy?
- What marketing channels are the most popular?
- What are competitive prices for the market?
- Do you already have visitors in these regions?
While it's tempting to expand into multiple countries at the same time, a better approach may be starting small and expand incrementally over time. You could start by expanding into Canada, the U.K. and Europe before moving to more distant or complex markets in Asia, South America or the Middle East. Local consultants can also provide valuable guidance.
Privacy Requirements
A growing number of countries have introduced privacy legislation designed to protect their citizens' personal data, including the United States with the California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 in 2020. When you expand into global markets, it's important to ensure that your website complies with these regulations to avoid costly fines and penalties.
The European Union's General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is the most visible example of these foreign laws. Beginning in May 2018, any businesses collecting data from EU citizens — including shipping information or payment details — must adhere to practices designed to protect their information. There are significant penalties for violating the new law.
Some important factors to address include:
- Users should be required to tick checkboxes to agree to terms or conditions rather than having them pre-ticked.
- You should only collect the data that you need (e.g. do you really need the shipping address' phone number?).
- You should have a clear way for users to both unsubscribe and delete all of their personal information from your servers.
- You should ensure that your partners adhere to the same GDPR-compliant standards that you do.
The best way to ensure compliance is to work with one of a growing number of GDPR and/or privacy consultants — especially those that specialize in ecommerce. Using tools like WonderProxy, you can test your website to ensure compliance in specific countries or regions and rest assured that you won't face the potentially-devastating penalties of non-compliance.
Payment Processing
Credit cards are the most popular payment method worldwide, but you may have to pay certain international fees. These fees typically depend on your business' location and the location of your card issuing institution. You should factor these fees into your international pricing in order to ensure consistent profit margins for your business when selling abroad.
The two most common international credit card fees include:
- Domestic cross border fees: The fee incurred when a transaction occurs in the business' registered country but the issuing bank is located in another country. These may also be known as International Service Assessment Fees (ISA) and range from 0.6% to 0.8% depending on the credit card brand.
- Foreign cross border fees: The fee incurred when a transaction is processed in a currency other than U.S. dollars. These fees range from 1% to 1.2% depending on the credit card brand.
While it's possible to only support credit cards, you can maximize your conversion rates by accepting popular local payment methods. One-fifth of Japanese shoppers prefer to make online payments using Konbini, which enables them to pay for online goods at local convenience stores. Spain and other European countries prefer bank transfer services.
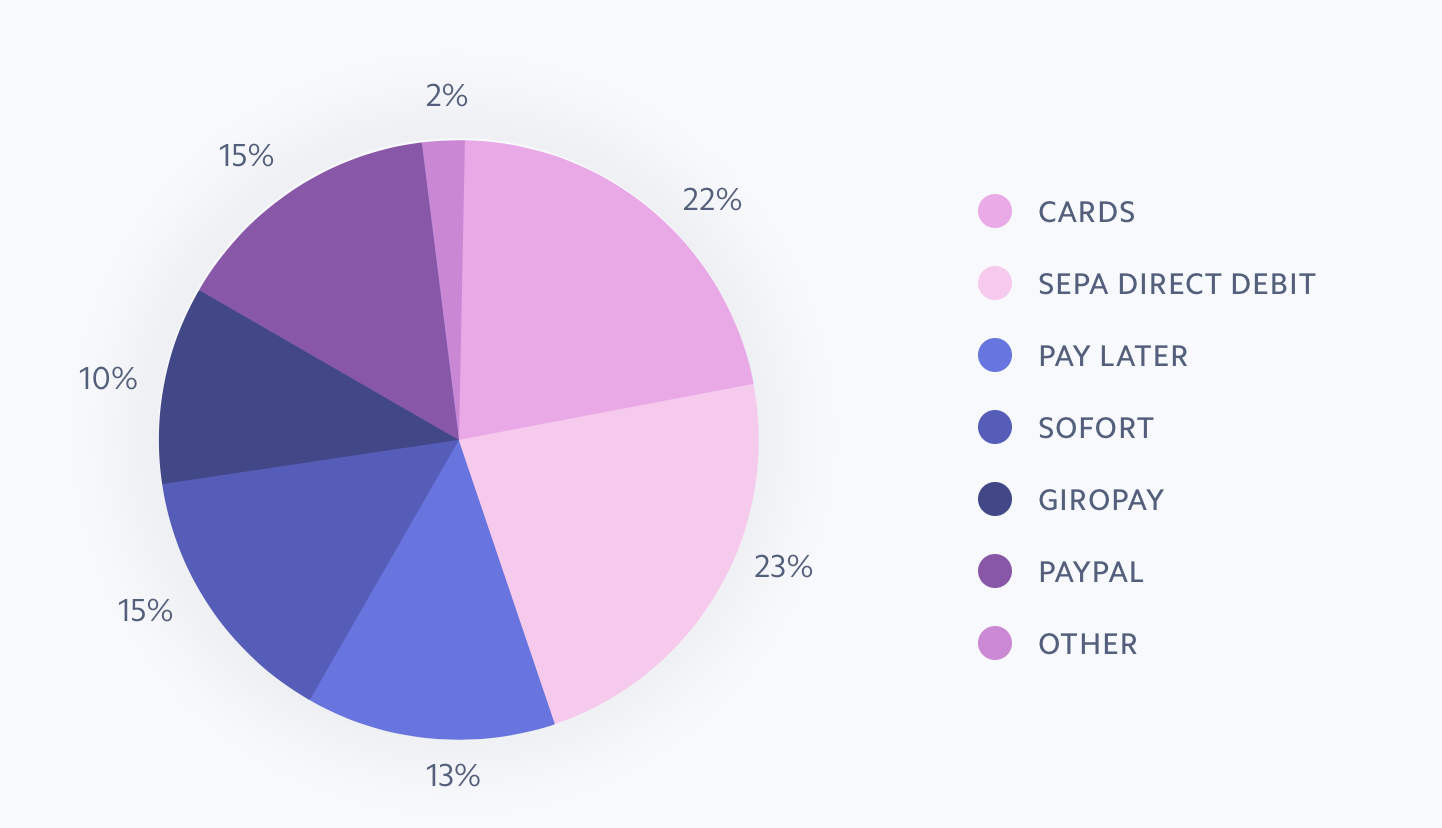
Breakdown of Common Payment Methods by Usage - Source: Stripe
Fortunately, many merchant accounts support multiple payment methods. For instance, Stripe accepts both credit cards and other popular forms of payment depending on the country. You can customize your shopping cart to show these payment methods for customers in certain countries at checkout in order to avoid showing unavailable payment methods for everyone.
WonderProxy is a great way to test payment pages to ensure that the proper payment methods and shipping methods are displayed based on a visitor's location. You can even integrate these tests into continuous integration processes to ensure that new code changes don't cause any issues and inadvertently break this functionality and hurt conversion rates.
Shipping & Fulfillment
International shipping has become a lot easier over the past decade with the rise of international shipping firms and local marketplaces offering local fulfillment. That said, it's still important to understand how taxes, customs, tariffs and other legal requirements work before shipping to international customers to avoid any unexpected surprises.
There are three ways to ship around the world:
- International carriers, including FedEx, DHL and UPS, provide door-to-door tracking and guaranteed prices, which make them the most convenient option for many ecommerce shops.
- National carriers, including national post offices, tend to offer the lowest prices, but they usually don't provide door-to-door tracking and may not be very reliable.
- International freight forwarders have the highest prices, but they handle shipments from beginning to end. You don't have to worry about customs or other thorny issues.
If you're looking to test a local market, you may want to consider online marketplaces that provide fulfillment. These services are similar to Amazon FBA in the United States, where they house products for fulfillment when purchased through the marketplace. You can then transition successful products to higher-margin direct sales or a combination of the two.
The Bottom Line
Expanding into international markets requires careful planning, but it's a promising way to grow sales beyond domestic markets. While we've covered many of the basics in this article, it helps to talk with local experts within a target country to ensure that you're fully compliant with all legal requirements and marketing to potential customers in the most effective ways.
Explore WonderProxy's plans today and see how easy it is to test your website and maximize the benefits of localization.